How to analyse cables and suspension bridges
Cables are used in transmission lines, rope ways and suspension bridges. Cable takes parabolic shape when it is subjected to uniformly distributor load. the central depot of the cable varies from 1/10 to 1/12 of the span. Suspension cables are provided with two types of supports at the ends either the cable pass over Pulley or cable pass over saddle. Shape of cable depends on type of load in carries and position of loads. To retain the shape of cable it is stiffened with stiffening girders in case of suspension bridges.
There are two types of stiffening girders,
- Three hinged stiffening girder
- Two hinged stiffening girder
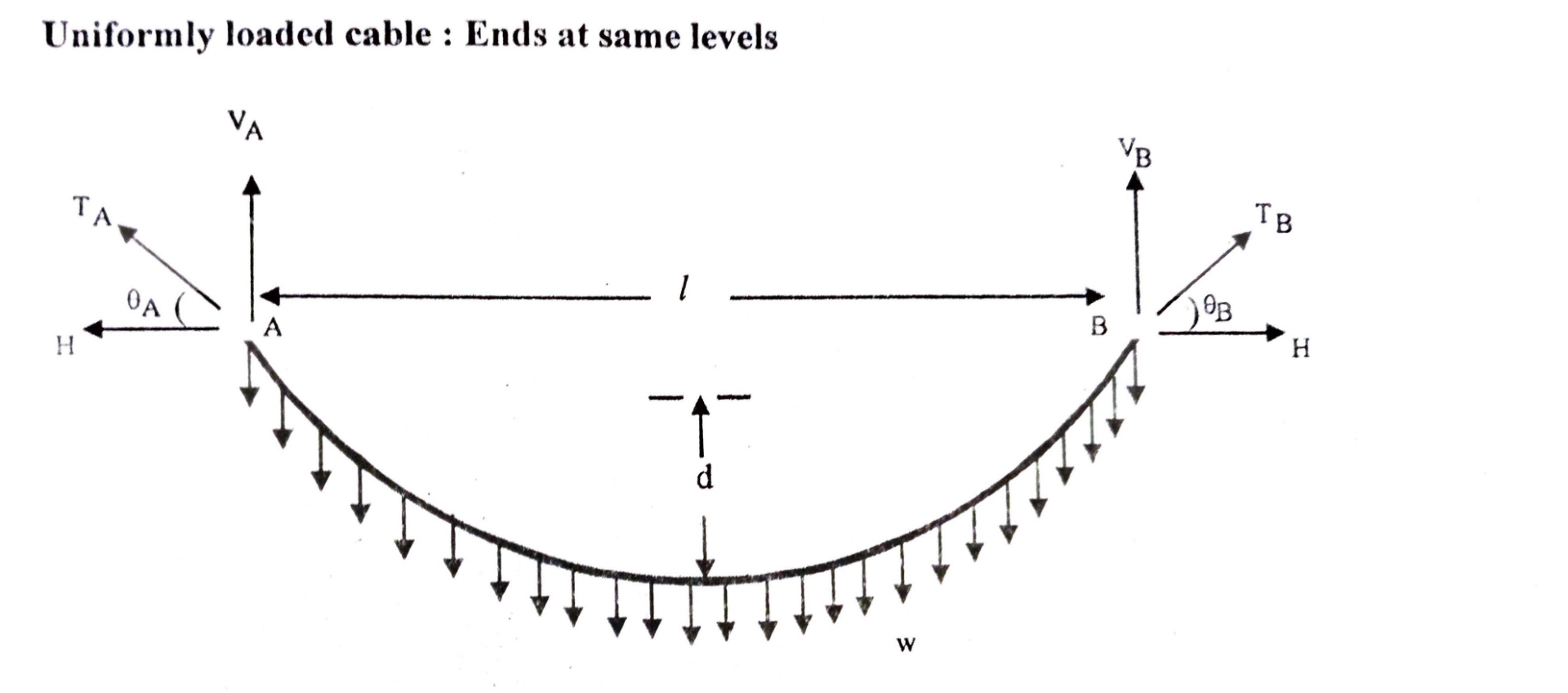
Moment about support at A
-Vb x l + w x l x l/2 = 0
Therefore Vb = wl/2
Moment about support B
VA x l – w x l x l/2 = 0
Therefore VA = wl/2
Since the cable is flexible, bending moment at anywhere in the cable is zero.
Take moment about maximum Dip point,
VA x l/2 – W x l/2 x l/4 -H x d = 0
wl/2 x l/2 – wl2/8 -Hd = 0
wl2/4 – wl2/8 – Hd = 0
Hd = wl2/4 – wl2/8
Hd = wl2/8
H = wl2/8d

No comments yet. Be the first to comment!